Table Of Content
The material found on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be used for diagnosis or treatment purposes. So, the researchers decided to look at how the amount of sleep and caffeine influence test performance. “It is true that when two manipulations are operating simultaneously, it is impossible to disentangle their effects completely,” explain authors Breckler, Olson, and Wiggins in their book Social Psychology Alive. Please list any fees and grants from, employment by, consultancy for, shared ownership in or any close relationship with, at any time over the preceding 36 months, any organisation whose interests may be affected by the publication of the response.
5.1. Correlational Studies With Factorial Designs¶
As with simple designs with only one independent variable, factorial designs have the same basic empirical question. Did manipulation of the independent variables cause changes in the dependent variables? However, 2x2 designs have more than one manipulation, so there is more than one way that the dependent variable can change. Thus, case‐control studies can also be hypothesis testing studies and therefore can suggest a causal relationship but cannot prove. It is less expensive and less time‐consuming than cohort studies (described in section “Cohort study”).
Optimization of the extraction process of minerals from Salvia officinalis L. using factorial design methodology - ScienceDirect.com
Optimization of the extraction process of minerals from Salvia officinalis L. using factorial design methodology.
Posted: Fri, 11 Oct 2019 10:48:34 GMT [source]
Clinical research study designs: The essentials
With this type of study design a pattern is usually adopted, such as, selection of subjects and controls on certain days of the week. Depending on the approach adopted, the selection of subjects becomes predictable and therefore, there is bias with regards to selection of subjects and controls that would question the validity of the results obtained. A nested case‐control study consists of defining a cohort with suspected risk factors and assigning a control within a cohort to the subject who develops the disease.10 Over a period, cases and controls are identified and followed as per the investigator's protocol.
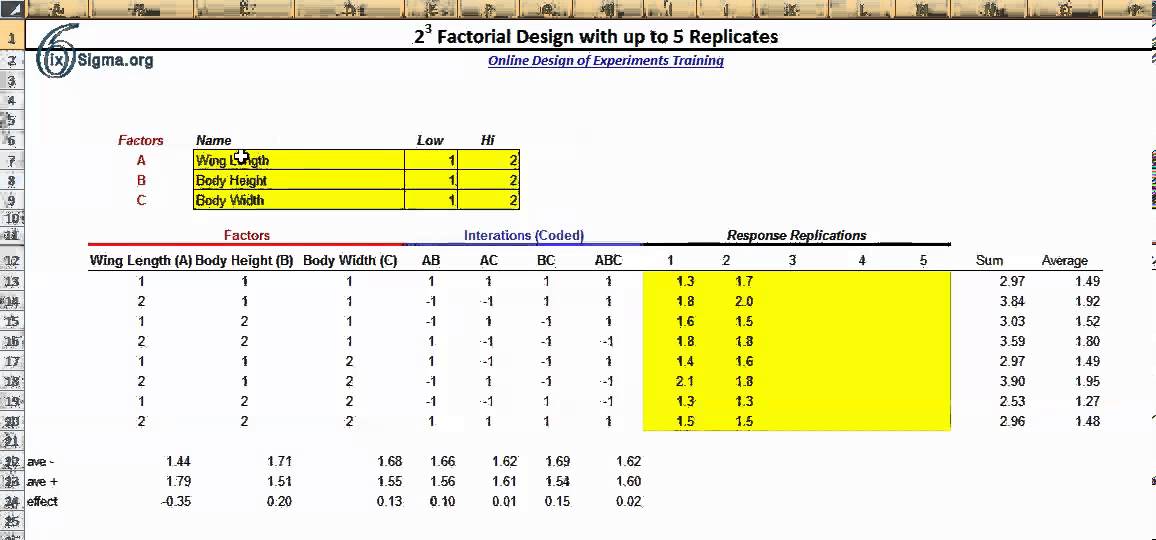
Minitab Example for Centrifugal Contactor Analysis
If one of the independent variables had a third level (e.g., using a handheld cell phone, using a hands-free cell phone, and not using a cell phone), then it would be a 3 × 2 factorial design, and there would be six distinct conditions. Notice that the number of possible conditions is the product of the numbers of levels. A 2 × 2 factorial design has four conditions, a 3 × 2 factorial design has six conditions, a 4 × 5 factorial design would have 20 conditions, and so on.
Certainly any research evaluation of intervention effectiveness can pose analytic and interpretive challenges. However, some challenges are of particular relevance to factorial designs. The researchers then decided to look at three levels of sleep (4 hours, 6 hours, and 8 hours) and only two levels of caffeine consumption (2 cups versus no coffee). When compared to the one-factor-at-a-time design (OFAT), factorial designs are less expensive, more efficient, and produce more comprehensive results.
Community trial
Other useful exploratory analysis tools for factorial experiments include main effects plots, interaction plots, Pareto plots, and a normal probability plot of the estimated effects. A factorial experiment allows for estimation of experimental error in two ways. The experiment can be replicated, or the sparsity-of-effects principle can often be exploited. Replication is more common for small experiments and is a very reliable way of assessing experimental error. When the number of factors is large (typically more than about 5 factors, but this does vary by application), replication of the design can become operationally difficult. In these cases, it is common to only run a single replicate of the design, and to assume that factor interactions of more than a certain order (say, between three or more factors) are negligible.
α-Fe2O3/Nb2O5 mixed oxide active for the photodegradation of organic contaminant in water: Factorial experimental ... - ScienceDirect.com
α-Fe2O3/Nb2O5 mixed oxide active for the photodegradation of organic contaminant in water: Factorial experimental ....
Posted: Sat, 02 Nov 2019 06:56:32 GMT [source]
3.3. Interactions¶
All of the plots will pop-up on the screen and a text file of the results will be generated in the session file. The next step is selecting which terms will be analyzed for the responses. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
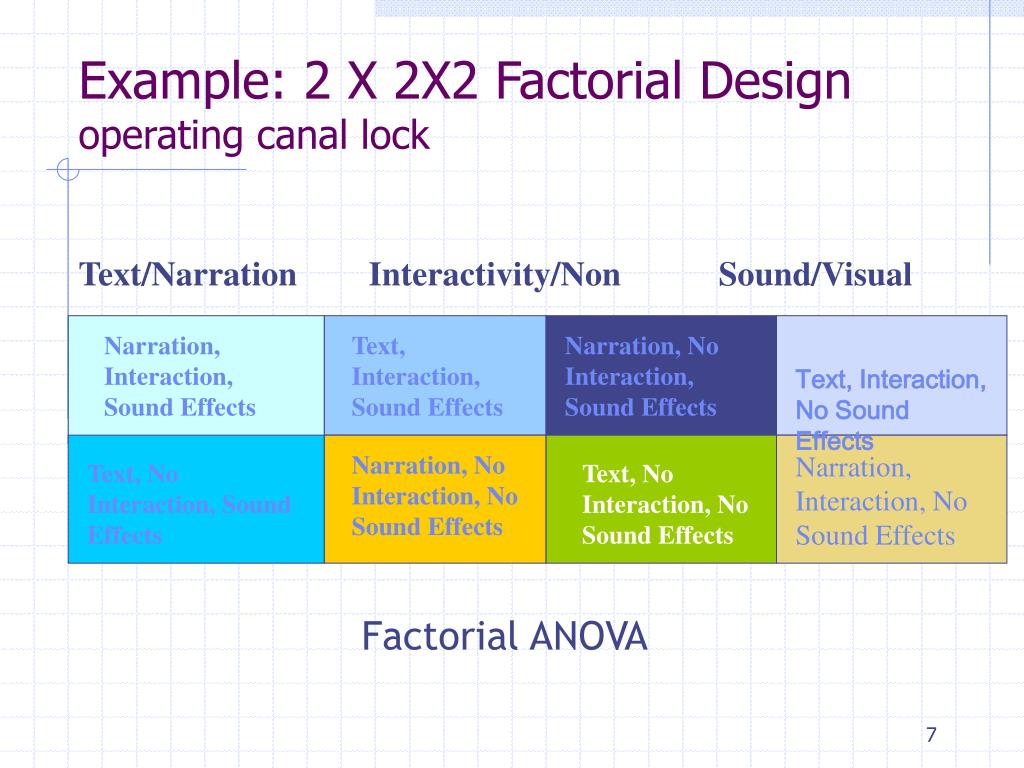
Table 1.
One of the earliest clinical trial studies was performed by James Lind et al in 1747 on sailors with scurvy.12 Lind divided twelve scorbutic sailors into six groups of two. The group who ate two oranges and one lemon had shown the most sudden and visible clinical effects and were taken back at the end of 6 days as being fit for duty. During Lind's time, this was not accepted but was shown to have similar results when repeated 47 years later in an entire fleet of ships. Based on the above results, in 1795 lemon juice was made a required part of the diet of sailors. Thus, clinical trials can be used to evaluate new therapies, such as new drug or new indication, new drug combination, new surgical procedure or device, new dosing schedule or mode of administration, or a new prevention therapy.
3.5. Identifying main effects and interactions¶
In block randomization, the subjects of similar characteristics are classified into blocks. The aim of block randomization is to balance the number of subjects allocated to each experiment/intervention group. For example, let's assume that there are four subjects in each block, and two of the four subjects in each block will be randomly allotted to each group. Therefore, there will be two subjects in one group and two subjects in the other group.17 The disadvantage with this methodology is that there is still a component of predictability in the selection of subjects and the randomization of prognostic factors is not performed. However, it helps to control the balance between the experiment/intervention groups.
For example, it is possible that measuring participants’ moods before measuring their perceived health could affect their perceived health or that measuring their perceived health before their moods could affect their moods. So the order in which multiple dependent variables are measured becomes an issue. One approach is to measure them in the same order for all participants—usually with the most important one first so that it cannot be affected by measuring the others.
I will propose an experiment to measure conditions that are required to produce hangriness. The pretend experiment will measure hangriness (we ask people how hangry they are on a scale from 1-10, with 10 being most hangry, and 0 being not hangry at all). The first independent variable will be time since last meal (1 hour vs. 5 hours), and the second independent variable will be how tired someone is (not tired vs very tired).
A 2 means that the independent variable has two levels, a 3 means that the independent variable has three levels, a 4 means it has four levels, etc. To illustrate, a 3 x 3 design has two independent variables, each with three levels, while a 2 x 2 x 2 design has three independent variables, each with two levels. Experimentwise error may be more of a problem in factorial designs than in RCTs because multiple main and interactive effects are typically examined.
No comments:
Post a Comment